When you are figuring out the right laptop for you and going through the available choices, the most important talking point would be the processor, also referred to as the CPU or the chip.
Intel and AMD make the laptop processors predominantly. Between them, there are many processors and generations within each processor. You might also be noting each processor has its own code names, which might be further confusing when you narrow down your machine. Here let’s try to decode the processor names and what various alphanumeric characters means.
Intel Processors
Intel’s main processor lineup are the Core i3, Core i5, Core i7, Core i9 and the latest Core i11 (you spotted the odd number sequence! while there is no official explanation, I assume it came in practice to avoid the initial Core2 Duo and Core2 Quad lineups) Coming back to the lineup, the Core i3 is the least powerful and it would be obvious to say with each ascension the CPU got powerful, with the Core i11 now the most powerful available.
Ok now that the first part is understood. You will see various alpha numeric strings added to the chip moniker. Let’s decipher it.
Let’s take for example – Intel Core i5-10510U.
Now you know the first part, the CPU is i5 chip. Let’s see what’s the string that follows. The first number(s) are the generation indicator, in our example, it is a 10th generation chip. Suppose you come across i5-5510U, it would imply 5th generation chip, which is an older generation compared to the 10th. So between these two, the 10th generation would be more powerful.
For the majority of Intel processors, the final three digits of the product number are the SKU. SKUs are generally assigned in the order in which processors in that generation and product line are developed. A higher SKU within otherwise-identical processor brands and generations will generally have more features. However, SKU numbers are not recommended for comparison across different generations or product lines.
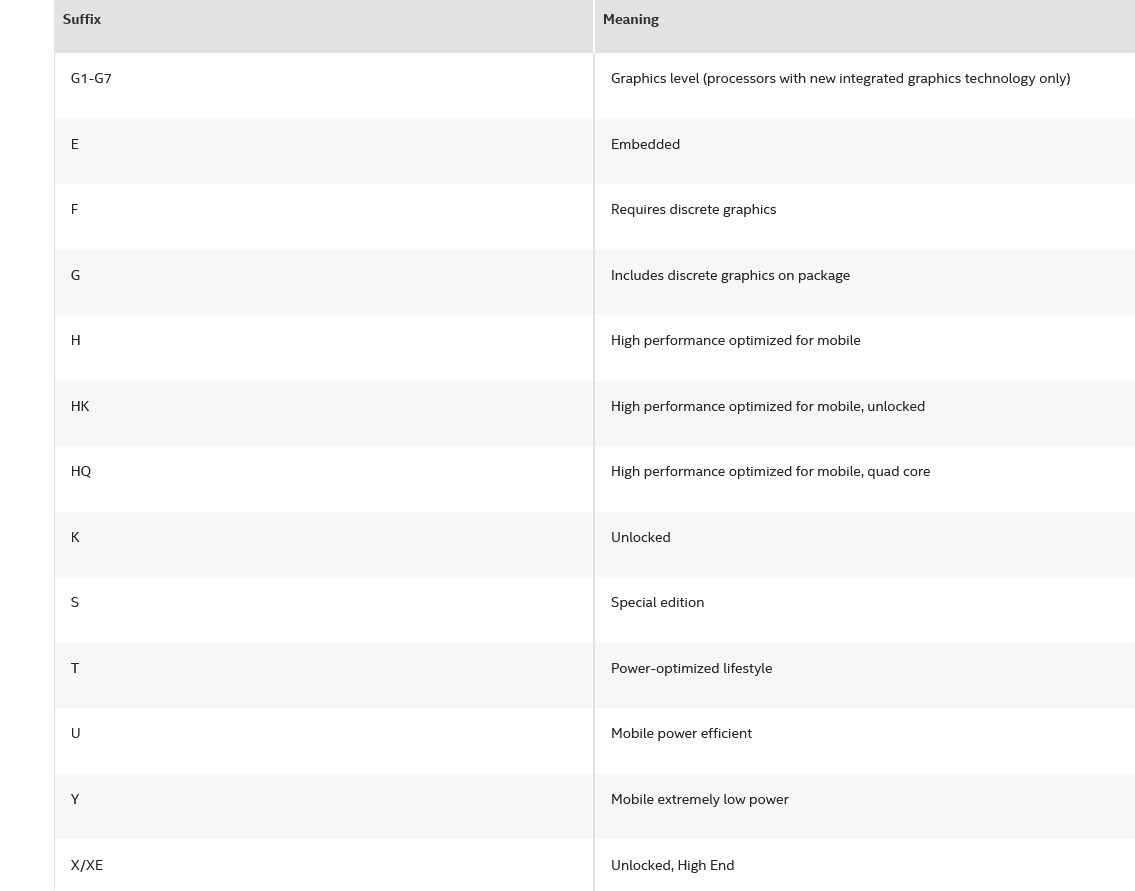
The alphabet that follows actually gives out more information on the particular chip efficiency. In our example, we have U in the suffix. Usually, when you are looking for laptops you might find models with the suffix U, Y, H and G.
Y series chips are highly battery optimized but come at the expense of performance. I would ideally, avoid machines with the Y series unless the battery is your key priority. The ideal pick would be the U series which are “power-efficient” they offer a midway between power and performance balance. If performance is your priority, look out for H series chips. G at the end indicates inclusion of discrete graphics on package.
AMD Processors
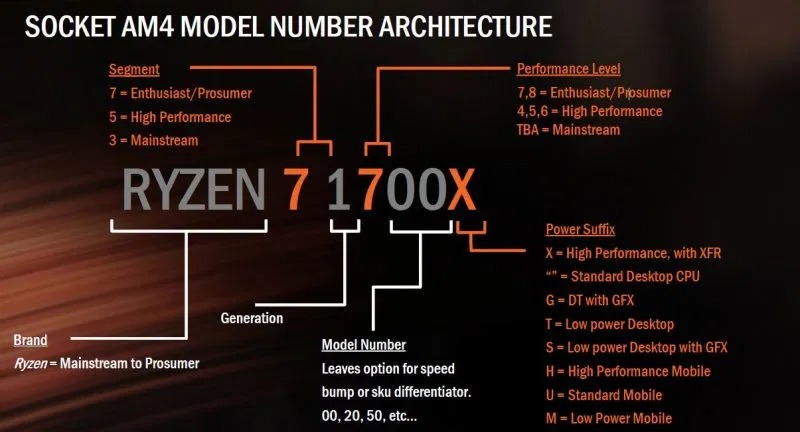
AMD uses Ryzen as the primary name for its CPUs. The naming convention is similar to Intel. You also have a similar odd sequence.
There are four different AMD Ryzen processor for laptops. The performance increases as you go higher up the order.
- Ryzen 3 — Up to 4-core processors.
- Ryzen 5 — Up to 6-core processors.
- Ryzen 7 — Up to 8-core processors.
- Ryzen 9 — Up to 16-core processors
The strings indicate the generation (higher the better) followed by a performance level, model number and power suffix.
So hope this sorts a bit of your doubts when narrowing down your laptop.